WIP
What if we provide Sites.Selected App permissions to SharePoint Admin Site?
TBP
WIP
What if we provide Sites.Selected App permissions to SharePoint Admin Site?
TBP
Sites.Selected MS Graph API permissions were introduced by Microsoft in March 2021. It was a good move towards site-level access for non-interactive (daemon) applications, but still developers were limited with only what MS Graph API provides for SharePoint. SharePoint CSOM and REST API still provides much more than MS Graph API.
So developers had to use AppInv.aspx at site level to provide ACS-based permissions to their apps to be able to use SharePoint CSOM and REST APIs. The bad news is ACS-based permissions have some downsides so some SharePoint/m365/security engineers consider them legacy and deprecated. But if we decide to disable SharePoint App-only service principals – all apps with ACS-based permissions provided via AppInv.aspx will stop working.
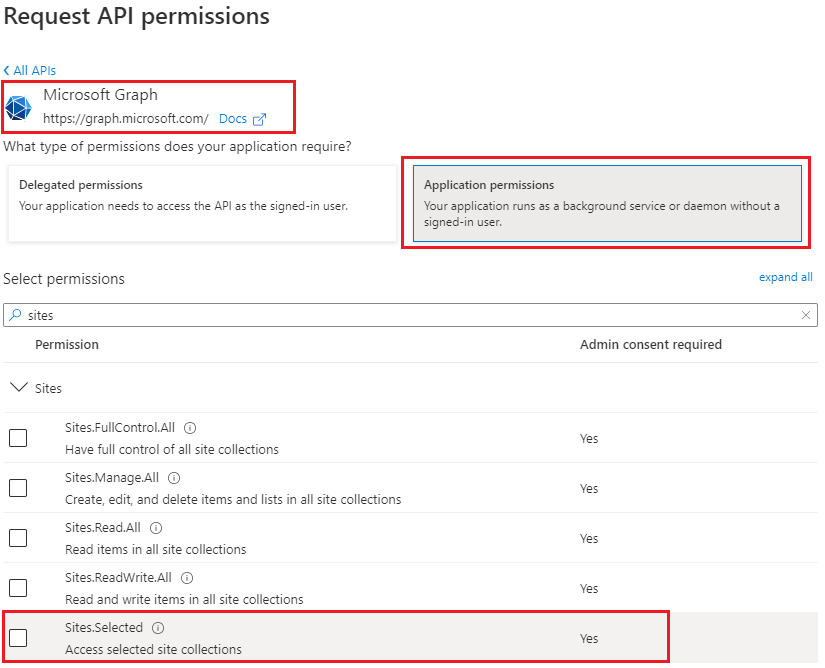
Recently Microsoft introduced Sites.Selected SharePoint API permissions for registered Azure Apps! So from now developers should be fully happy with API permissions provided in Azure (without SharePoint ACS-based permissions).
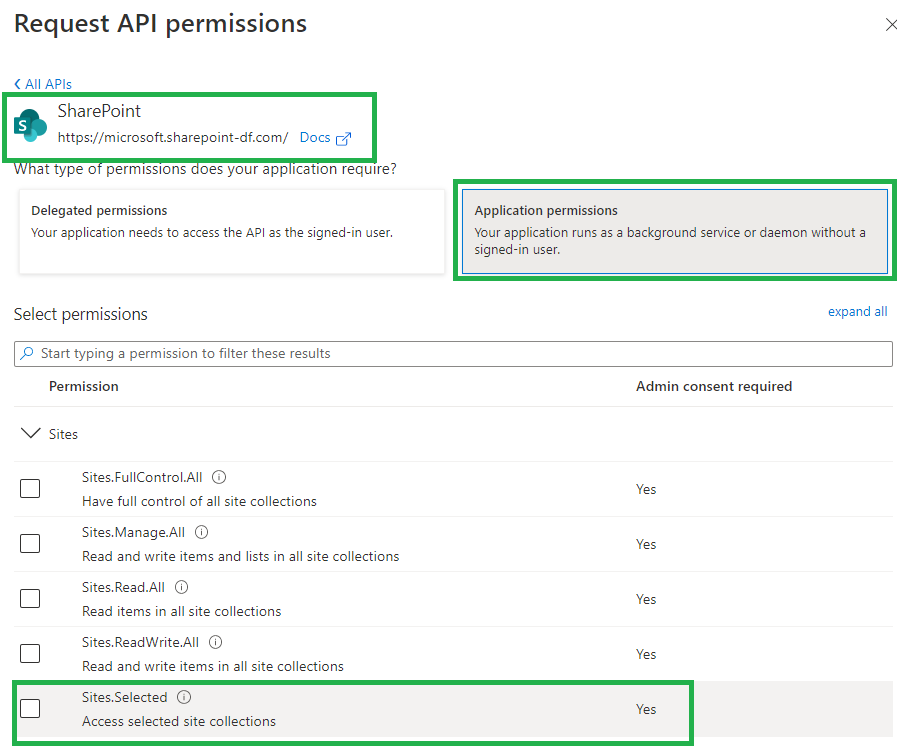
Why is this so important? Because this should allow us to be able to switch from ACS based permissions provided in SharePoint via AppInv.aspx to Azure-provided permissions and as a consequence – disable SharePoint-Apps only principal (‘set-spotenant -DisableCustomAppAuthentication $true’).
Why we are eager to disable Custom App Authentication in SharePoint? Simply say, SharePoint App-only service principals are not trackable (they all appeared as a “app@sharepoint.com” id in all logs) and hard to manage (there is no way to get list of existing/registered SP app-only service principals, sites and their owners) – see more in this article. (Update: there are tools – check Azure ACS retirement: Track down ACS apps).
So, SharePoint Sites.Selected application API permissions provided in Azure is a significant step to make Microsoft 365 SharePoint environment more secure and manageable.
Since Feb 2024 Microsoft supports also delegated Sites.Selected permissions. Delegated Sites.Selected permissions are assigned the same way as application Sites.selected permissions – through the /permissions endpoint. You still assign only the application id and role. When the call is made the permissions are calculated either as application or delegated, and assuming the request is authorized it will go through.
Microsoft implemented granular permissions ( e.g. to a list, item or file) alongside with Sites.Selected permissions. Original implementations of Sites.Selected allowed access to entire site collection only. With new ‘Lists.SelectedOperations.Selected’, ‘ListItems.SelectedOperations.Selected’ and ‘Files.SelectedOperations.Selected’ permissions it is possible to provide application permissions to list, library or list item or particular document (reference).
Details To Be Provided…
Since the beginning of 2024 Microsoft supports Delegated Sites.Selected API permissions. This is to support security best practices – the minimally possible access should be provided. I.e. the idea is: even Sites.FullControl.All delegated permissions allows access not to all sites, but to sites current user was provided access to, it would be a good idea to restrict access with only sites this specific app is required access to. That’s good.
Update: Sites.Selected API MS Graph permissions was introduced by Microsoft in 2021. It was a good move towards site-level development, but still developers were limited with only what MS Graph API provides for SharePoint dev.
So devs had to use AppInv.aspx at site level to provide ACS permissions to their apps to be able to use SharePoint CSOM and REST APIs.
Recently Microsoft introduced Sites.Selected SharePoint API permissions for registered Azure Apps! So now devs should be fully happy without ACS-based permissions.
You have an application that needs access to Microsoft 365 SharePoint Online site/list/documents. Application is running without interaction with users – e.g. unattended, as daemon job.
There are two options you can authenticate to Microsoft 365 – with the secret or with the certificate. Authenticating with certificate is considered more secure.
Note: we will use PowerShell 7.2 and PnP.PowerShell 1.9 to illustrate it.
If SharePoint-Apps only principal is disabled in your tenant
(i.e. ‘Get-PnPTenant | select DisableCustomAppAuthentication’ returns $true ), then the only way you work with SPO from code is:
In all other cases (even your Connect-PnPOnline command complete successfully) – you will be getting error 401 (unauthorized) when trying Get-PnPTenant or Get-PnPTenantSite or Get-PnPSite
If SharePoint-Apps only principals are enabled in your tenant
(i.e. ‘Get-PnPTenant | select DisableCustomAppAuthentication’ returns $false ), then you have three options to work with SPO from code:
There are three Yammer APIs that I know:
There were also rumors on (in development/preview) Yammer REST API v 2.0 – https://api.yammer.com/ – but nothing specific…
Classic Yammer REST API is rich and mature, but Microsoft said that no further updates are planned on classic Yammer API, so here is my article on how to call Classic Yammer API from code, including search in Yammer … Since Microsoft Graph API for Viva Engage (Yammer is very limited), we have to rely on classic Yammer Viva Engage API, including search through Viva Engage communities posts.
You’d call this classic API with your personal credentials, i.e. if operation requires admin access, you’d need activate your Yammer Admin role.
Update (Message ID MC1045211, Published Mar 31, 2025): Microsoft Viva Engage will retire the private content mode by June 30th, 2025.
This also affects (classic) Yammer API.
E.g. before June 30th, 2025: as Yammer admin, you were able to activate private mode and get access to all Yammer communities via Yammer API.
E.g. before June 30th, 2025: as Yammer admin, you will need to be a community (Microsoft 365 group) member or owner to access community content.
So far the only available operations are:
You also can work with communities membership – add/get/delete members – but it’s done via groups API
Authentication options available – delegated and application (e.g. automation available), with Entra Id App Registration.
Provides summary and activities
Authentication options available – delegated and application (e.g. automation available), with Entra Id App Registration.
more on the subject (to be explored…)
There are two permissions you can provide to your azure app registration:

There are scenarios when you need to pull only newly created SharePoint sites, e.g. get sites created since yesterday or get last 100 created sites. Usually other articles and existing PowerShell scripts solve this by pulling all sites from tenant and then iterating through sites to get only new sites. That approach is not nice and simply does not work in large environments. How can we get only sites created recently, not all sites? Here is how I use Microsoft Graph API to get only new sites.
Update (6/28/2024): Microsoft announced updates to it’s delta API for SharePoint, so I added option 3 – see below.
Let say you administer Teams, OneDrive and SharePoint Online in a Microsoft 365 tenant. You have a pretty big environment – ~10k or more sites and you want to quickly find just new SharePoint sites or teams (e.g. sites created recently – during last hour/day/week/month). This might be required for ad-hoc reports and for automation scenarios – like applying required configurations or assign some property value to all newly created sites.
With GUI it’s done easily: SharePoint Admin Center -> Active Sites -> sort based on “Date Created” – done.
With PowerShell – not so simple.
“Get-PnPTenantSite” cmdlet returns a site object but the object does not have “Created” field. It’s a web property (not site property). But to get a web object – you have to connect separately to each site and get root web object to check when the web was created. For small environments it is possible, for large environments it can take days… And still not nice.
“Get-PnPTenantSite” with “-Filter” option would help, but “…Currently, you can filter by these properties: Owner, Template, LockState, Url.”
Get-SPOSite – similar experience.
Teams + Exchange modules can help a little:
Get-Team | select GroupId | % { Get-UnifiedGroup $_.GroupId | select DisplayName, WhenCreated } | sort WhenCreatedbut… 1) it’ll give you group-based sites only 2) it is not easy to automate 3) this might take long for large environments. I know much better solution:
Microsoft Graph API helps. It returns result in seconds and you can sort or filter results based on created date . Below are two methods: Option 1 is based on Search and filtering and Option 2 is based on Sites Search and sorting. So there are some pros and cons for each method.

Entry point: https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/search/query
Microsoft Graph Search API allows KQL in queries. So we can form a query with something like “created>=1/1/2021” and use entity type = ‘[“site”]’. Search should return only sites created after Jan 01, 2021.
Check PowerShell script sample here: Get-NewSites.ps1
https://github.com/VladilenK/PowerShell/blob/main/reports/SharePoint/Get-NewSites.ps1
If you are getting more than 500 results – think of paging.
Entry point: https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/sites
This option is also based on Microsoft Graph API, but sites entry point, which allows search too and sort results by property “createdDateTime”. So we will just search for everything and select how many results we need based on createdDateTime property.
Check PowerShell script sample here: Get-NewSites.ps1
https://github.com/VladilenK/PowerShell/blob/main/reports/SharePoint/Get-NewSites.ps1
You can use “Get delta” under SharePoint Graph API – check for details here. It says “Get newly created, updated, or deleted sites without having to perform a full read of the entire sites collection”. I’ll do my own testing, but for now check this:
Video: Microsoft Graph Delta Capabilities in SharePoint API
Yammer (now Viva Engage) is an internal (corporate) social network, and part of the Microsoft 365 suit of services. How do we work with Viva Engage programmatically? Can we read messages or search through communities? Can we get groups (communities) details and membership – etc. Is there an API we can use? How do we authenticate? Here you go.
There are two API’s available to work with Viva Engage (Yammer) from code:
Microsoft Graph API is a preferred way to work with Viva Engage programmatically. You’d just need an Entra Id App Registration configured correctly to authenticate and be authorized to call Graph API:
Unfortunately, Microsoft Graph API is still limited (Mar 2025) with respect to Viva Engage – you can only do CRUD operations against communities. You cannot search through community messages, you cannot post messages or read what is posted. You cannot reply or react on messages.
Since any Yammer community membership is based on Microsoft 365 group – you can use all group operations (including managing membership).
Since any Yammer community has a SharePoint site behind – you can use SharePoint Graph API to manage community documents.
Classic Yammer API is old, but still relevant API. With Classic Yammer API you can do what is not possible yet with Graph API, e.g. get messages (all or latest or within specific community or about some topic, etc.), search through messages, as well as post and delete messages.
Here is the full list of available operations. Unfortunately, Microsoft just keeps light on there (no plans for development). Below is how to authenticate to Yammer API and some usage samples of classic Yammer API for Viva Engage.
Update (May 2025): Private content mode will retire as of June 30th, 2025 (MC1045211)
This includes classic yammer API. Since Viva Engage (Yammer) communities access is now based on Microsoft 365 groups membership – you’d need to be a group member to access community messages via GUI or via classic Yammer API, (no exceptions after June 30th, 2025 MC1045211). Though export data will continue working as usual.
Navigate to the page: https://www.yammer.com/client_applications
Click “Register new application”:
Fill all the fields:
Client ID and Client secret will be generated automatically:
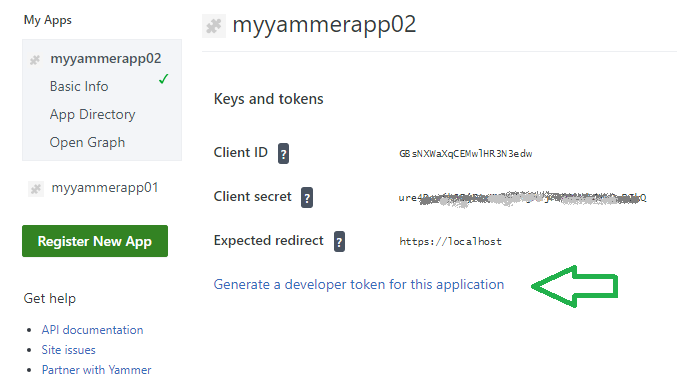
I’m not sure – how to get access token from Client ID and Client secret, so I use link “Generate a developer token for this application”. When you click this link, a token will be generated, and it says “Here is your personal token for testing. Please copy it somewhere safe as it will disappear when you leave the page:”
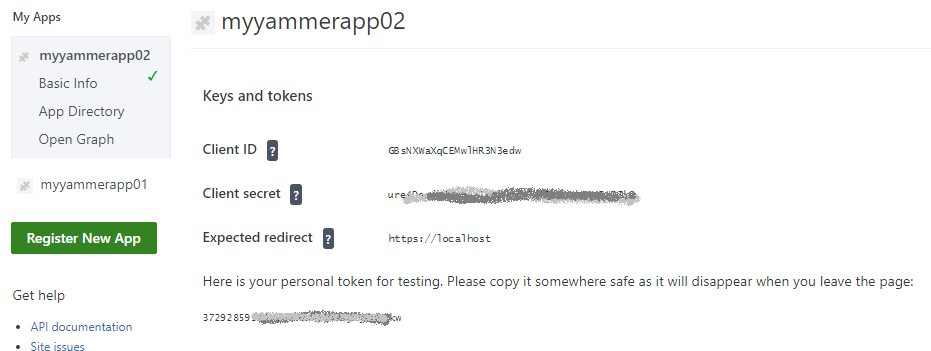
Once you get the toke – you can use it in your code (consider vaulting or other save methods). Here is an example based on powershell, but surely you can do the same with programming language you comfortable with:
$baererToken = "Put your token here"
$headers = @{ Authorization = ("Bearer " + $baererToken) }
# get messages
$webRequest = Invoke-WebRequest –Uri "https://www.yammer.com/api/v1/messages.json" –Method Get -Headers $headers
$results = $webRequest.Content | ConvertFrom-Json
$results.messages | ForEach-Object {
$message = $_
Write-Host "Message Id:" $message.id
Write-Host "Message body:" $message.body.parsed
}
# get users
Invoke-WebRequest –Uri "https://www.yammer.com/api/v1/users.json" –Method Get -Headers $headers | ConvertFrom-Json | select email
# search through Viva Engage messages
$YammerApiURL = "https://www.yammer.com/api/v1/search.json?search=Test*"
$results = Invoke-WebRequest –Uri $YammerApiURL –Method Get -Headers $headers | ConvertFrom-Json
$results
$results.count
$results.users[0]
$results.messages.messages[0].body.parsed
# export all messages (admin role required)
$url = "https://www.yammer.com/api/v1/export?since=2020-02-9T00:00:00+00:00"
$url = $url + "&model=Message&include=csv"
Invoke-WebRequest –Uri $url –Method Get -Headers $headers | ConvertFrom-Json
Your organization use Microsoft 365. You are implementing or configuring an Intranet Portal (Home Site). Search plays an important role here – you want search be relevant to the context – i.e.
Microsoft Bookmarks are working only at tenant level search – i.e. if you want bookmarks work on site level search – you need to set up site search scope as tenant.
So if you configure the Intranet Portal site (Home site) search scope to “site” or “hub” to limit results with site/hub content – you will loose “answers” functionality.
The solution is very simple:
Update Query field with KQL – e.g., with something like
(path:http//contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/IntranetPortal/ OR path:http//contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/CompanyNews/ OR path:http//contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/Onboarding)/)
to get results only from “Intranet Portal” and “Company News” sites.
Keep in mind that this will affect all other SharePoint search entry points – SharePoint landing page, Office.com etc. – so although you can configure All (and Files) verticals, but it’s not recommended. It will confuse users – they expect to search for everything under “All” vertical. Instead, consider custom vertical – e.g. “Official” scope.
After configuring – It might take 1-24 hours for the change to take effect, depending on tenant size.
If you configure that at the tenant level – i.e., Microsoft 365 Administration -> Settings -> Search and intelligence -> Customizations -> Verticals
then search results will be trimmed everywhere – SharePoint Landing Page, Office landing page (Office.com), Office App, Bing search.
Teams search will not be affected as from Teams you only search for teams content. Same for Onedrive and Yammer.
If you want the “official” search results only under Intranet Portal and leave other search entry points unaffected – then
you need to configure the same at Home (Intranet Portal) site level: Site Settings -> Microsoft Search -> Configure search settings -> Verticals
and configure site search scope to site or hub scope. But in this case you will loose answers functionality.
Global search settings – like acronyms, bookmarks and verticals – works only if site search scope is tenant.
If site search scope is site or hub – then site-level search verticals will apply (and no answers functionality will be possible).
There might be two problems with that:
The solution is DepartmentId property:
Use DepartmentId={<Hub Site ID>} in the KQL qury and your search results will be limited to your hub content while answers will still be working too. You can even combine DepartmentId with other conditions to add more sites (that are not in hub) to search scope:
(DepartmentId={4965d9be-929b-411a-9281-5662f5e09d49} OR path:http//contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/Onboarding OR path:http//contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/CompanyNews)
It worth to mention, that DepartmentId is the property that propagated from the root of the hub site to all associated sites and their content – list items, documents and pages.
Another possible option would be – site property bag…
The ultimate goal is to provide users with “Official” results only. But official sites might not be all part of one Home site hub. We can include in All search vertical query 10, 50, 100 sites, but what if we have 10k official sites in enterprise – e.g. operated by different departments – and all of them might want to be present in search results.
So, how about – if the site is considered official – we create an indexed site property, e.g. “SiteIsOfficial” with a value “Yes”. Then we map the crawled property to a managed property – e.g. RefinableString89 – and use this managed search property in query – e.g. (SiteIsOfficial=Yes).
This is actually clever idea, but this does not work… This query would only return sites, not sites content. E.g. what was indexed as site object – will be included (including home page). But site items – i.a. documents, lists, other pages – all site content – will not be included…
So let’s get back to DepartmentId…
Again – the ultimate goal is to give users option to have “Official” results. But they still might want to be able to search through all content.
What if we rename the default “All” vertical to “Home Site” and configure query for official results only.
Then we can create a custom vertical called “Everything” or “All” with no query limitations to give users all reasults
Update: not a good idea either… If the home site search scope is tenant – so verticals are configured and be visible at tenant level – i.e. everywhere…
My personal preference is to keep All vertical as real All, and create a custom Vertical “Official” for official results only where we would use query trick.
In addition, it would be nice to highlight results from official sources by using custom result type – check “Manage result layouts for SharePoint results in Microsoft Search”
There is a new feature in Microsoft 365 SharePoint Online – “Restricted SharePoint Search“. With Restricted SharePoint Search you can restrict organization-wide search to a curated set of “allowed” SharePoint sites – sites that you have checked the permissions and applied data governance for.
UPDATE: this approach only works if the mobile number is stored in SPO UPA.
If the mobile number is stored in AAD only, the admin will need to remove the mobile number from AAD for the affected users.
UPDATE 2: In December 2024, Delve will be retired.
Scenario:
you administer SharePoint Online Microsoft 365 tenant
business asks you to remove mobile phone numbers from SharePoint User Profiles:
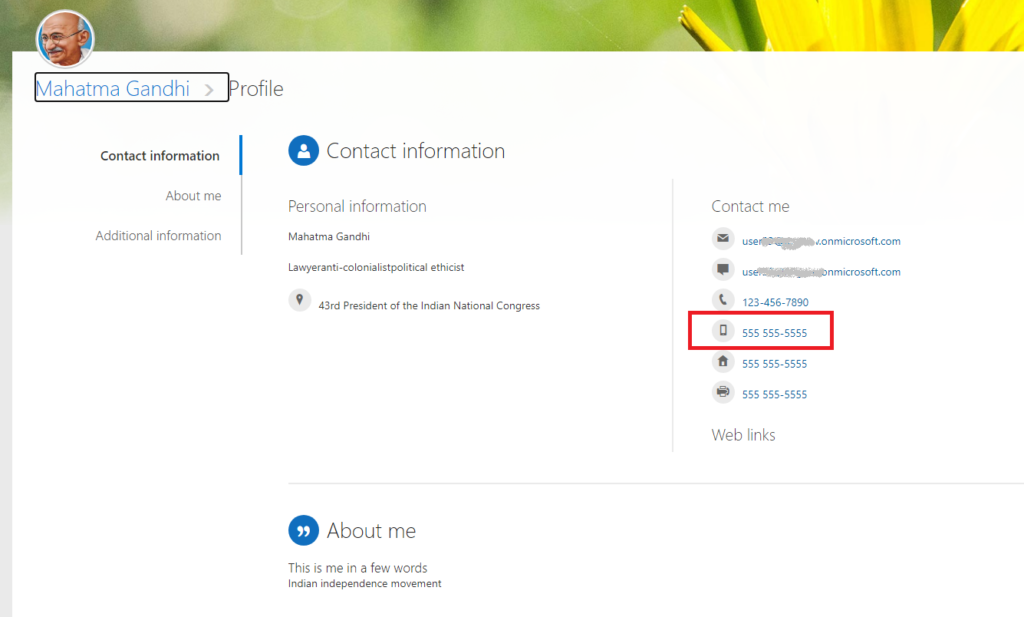
As a SharePoint administrator, you can do it:
1. Start Microsoft 365 SharePoint Admin Center
2. Navigate to More Features -> User Profiles -> Manage User Properties
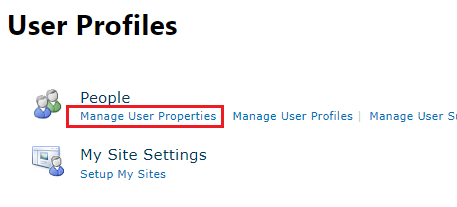
3. Under “Contact Information” -> Mobile phone -> Edit
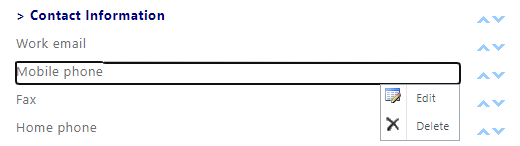
4. Uncheck “Replicable”, Save, wait a minute or two
5.
– Select “Default Privacy Settings”: “Only Me”
– Uncheck “User can override”
– Uncheck “Allow users to edit values for this property”
– Uncheck “Show in the profile properties section of the user’s profile page”
– Uncheck “Indexed”
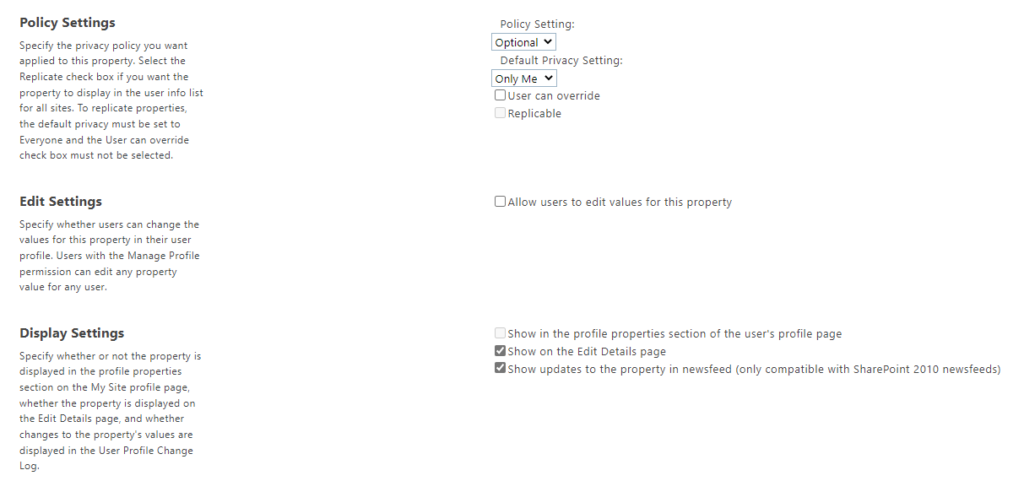
6. Save
Note: Microsoft implemented new MS-Graph API that adds or deletes profile card custom properties using the profile card API in Microsoft Graph
Resources:
I know that my country – the country where I was born and grew up, the country where my parents gave me everything – from first sip of milk to education and cultural upbringing, the country where I got my friends – this country is the best country in the world. But wait… Did you say “the world”? What is the world? Is it something where other people live? Do those people live their own ways and speak their own languages? Do they love their countries and their culture?
Of course, we know that there are other countries (we use internet-connected computers and smartphones). We probably heard/use words like Gastarbeiter, automobile, opera. But did you know they all came from different other languages to our language. Now what are the other languages and why do we learn foreign languages? I would say there are two main reasons.
The first one is just a practical reason that came from the past – knowing a foreign language helps you make more money. International trade is an essential part of the world economy and impossible without communication. So the ability to communicate in different languages simply gives you an advantage – an ability to do thing not everybody can do – and an opportunity to earn more.
The second reason lies more in the cultural or cognitive field. Simple example: How do I know that The Hamburgeris is tasty? Only because I tried other food and I can compare. The same with languages. “Wer fremde Sprachen nicht kennt, weiß nichts von seiner eigenen” – which means “Those who do not know foreign languages do not know anything about their own” stated the famous German poet and scientist Johann Wolfgang von Goethe.
And that is so true. I just started understanding it because I just started studying foreign language. And the more I learn it – the more I like it. The world is diverse. And that’s the beauty of it. And that diversity is expressed via languages. Each language is unique and beautiful as it absorbs all historical and cultural legacy of a nation.
So, knowing other languages not only benefits us with more opportunities and perspectives, but makes us more tolerant, open-minded, intelligent and creative.
Change is live. Static is death. Everything and everybody must change for live. The moment you stop developing – you are out. That’s true for everything starting from plants and animals. For human being that’s also true, but a little different. We are not competing for food any more. As a social creatures we want to be a part of the society, we need to be respected, recognized, useful. And that is done via job, via profession we choose.
In average we spent 8 hours a day at work. Some people might think that work time is distracted from our live because only after work you can have fun spending money hard earned during the work time when you have to do something unpleasant just to be able to do what you really want to do after work. Miserable and pitiful people they are. Eight hours a day is a decent part of our life. I do not want to waste that time. I want to enjoy that time. How do I enjoy that time? Choosing a profession that I love.
In a modern world one of the biggest problem mankind facing is a human health. And that is where I want to work. I know, that’s not easy. In order to be successful in the healthcare field, I need to pose certain skills and abilities. One of the essential skills is an ability to love people. I must be able to treat and respect my clients in order to maintain their trust and support. As well as readiness and acceptance. I have to be precise and confident in my actions. I have to be able to accept the consequences if something goes wrong. There may be times when an emergency occurs and the environment gets chaotic. But, on the other hand, what could be better, what could be more demanded and rewarding then help people live healthier lives?