There is was a known problem with Microsoft Delve. It’s not a technology problem though. (Upd: Delve is scheduled for retirement in Dec 2024)
We know SharePoint site permissions are not easy to manage. E.g. you can break permissions inheritance at any level – subsite, library, list, folder, list item or specific document. Anybody with full permissions can do that. The worst thing is there is was (*1) no native ability for site owner to get full site permissions report. We must have used third-party tools or PowerShell to have all permissions in one document.
So no wonder SharePoint sites were heavily over-exposed. Especially when a site owner tired with complexity of SharePoint permissions system decided to share resource with “Everyone”. And the other person, not knowing site is shared with everyone, might save some sensitive data. That is the real issue.
Now, what is Delve? It’s a service that
– get signals from allover Office 365 – who did what etc.
– based on that, using AI and Office Graph, generates suggestions – “what others do”.
Of course, Delve is security-trimmed, i.e. it will neve suggest you a document you do not have access to. But some sites might be overshared. Delve works as it should work – it suggests you documents it believes related to you (based on Microsoft Graph insights) and you already have access to.
Now bad thing happens – people start seeing documents they never new they have access to. Where are these documents from? Of course from sites shared with Everyone. Who to blame for the security breach? Delve? Microsoft Graph? Microsoft 365 SharePoint Online?
Strictly says, it is not Delve’s problem. It’s more human problem than technological.
Delve just does it’s job, and does perfectly. Delve simply displays the information already shared widely.
How do we solve the issue?
- Disable Delve?
- Disable search (stop sites crawling and remove results)?
- Restrict users who can provide signals via item insights privacy?
see Microsoft KBA on how to disable MS Graph for a specific User
Those methods are half-measure. Methods above are just hiding the problem – not solving it. Agree it helps stop the deterioration, bud does not fix the root cause.
How do we solve the real problem and what is the root cause?
- Of course, we need remove incorrectly provided permissions. How?
- Only site owner (data owner) knows which content should be shared with whom with which access rights. So we need to ask sites owners to review their permissions. How?
- First, we need a list of over-exposed sites. How?
- There are two methods (more details – check this article)
- Brute force – use PowerShell or 3-rd party tool to get permission report on all sites in tenant, select permissions provided for Everyone…
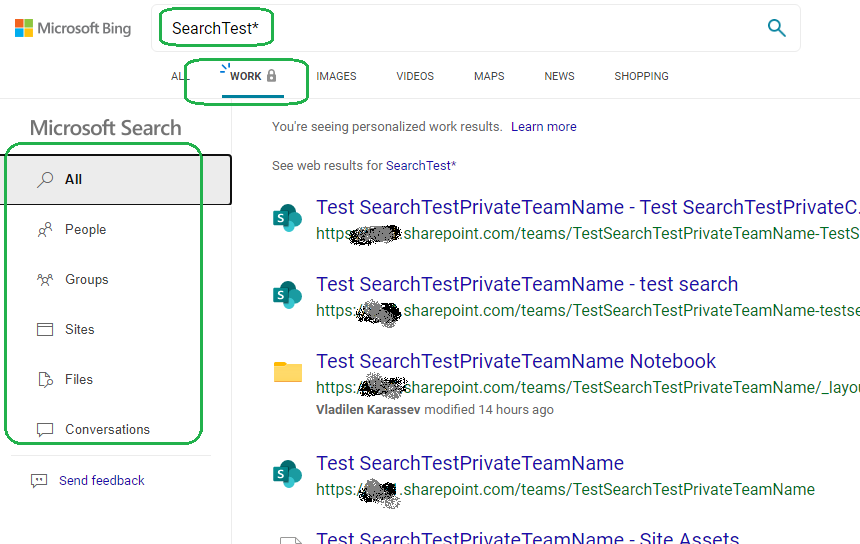
- Smart move – use Microsoft search. As search is security-trimmed, we can search for available content on behalf of a user with no permissions provided.
- Then we find owners for each wide-open site. How?
- for group-based sites we get member of the “owners” group
- for non-group based sites we get site collection administrators
- We would also sort sites by “is it supposed to be public?”. I.e. if the site was born as public – e.g. Public Team or Public Yammer community – or Communication site – maybe it’s less concern.
- It would be a good idea to bring DLP and/or automatic content sensitivity labelling, so we could start remediation from sites labelled as storing most sensitive data.
- Finally, we need to let site owner know that his site is Open to everybody and ask to fix it. How?
- e-mail communication
- SharePoint list containing overshared sites with owners, configured the yaw every person can see only sites he/she owns
- inform the site owner how to get full permissions report to his site,
e.g. KBA How To Get SPO Site Full Permissions Report
and video “Full Permissions Report for a Team SPO Site Owner“
References
- Governance tip on finding overshared content in O365/SharePoint by Mikael Svenson
- Report on file and folder sharing in a SharePoint site by Microsoft
- How to determine resources to which all external users have access by Microsoft
- How to get list of sites shared with Everyone
- How to Get full SPO Site Permissions report
Bill Baer’s on search and “prevent sensitive files from being exposed in search”