SharePoint Advanced Management is an add-on to Microsoft 365 for admins. Microsoft says that it is a powerful suite of tools for IT admins to bolster content governance throughout the Microsoft Copilot deployment journey. Let us have a closer look at what SharePoint Advanced Management (SAM) is how exactly it helps with governance enforcement in the Copilot era.
Microsoft recently updated SAM features (this KBA is based on Oct 2025 features set). Now Advanced management page has a dashboard – “Overview” tab and “All features” tab.
Advanced management – Overview
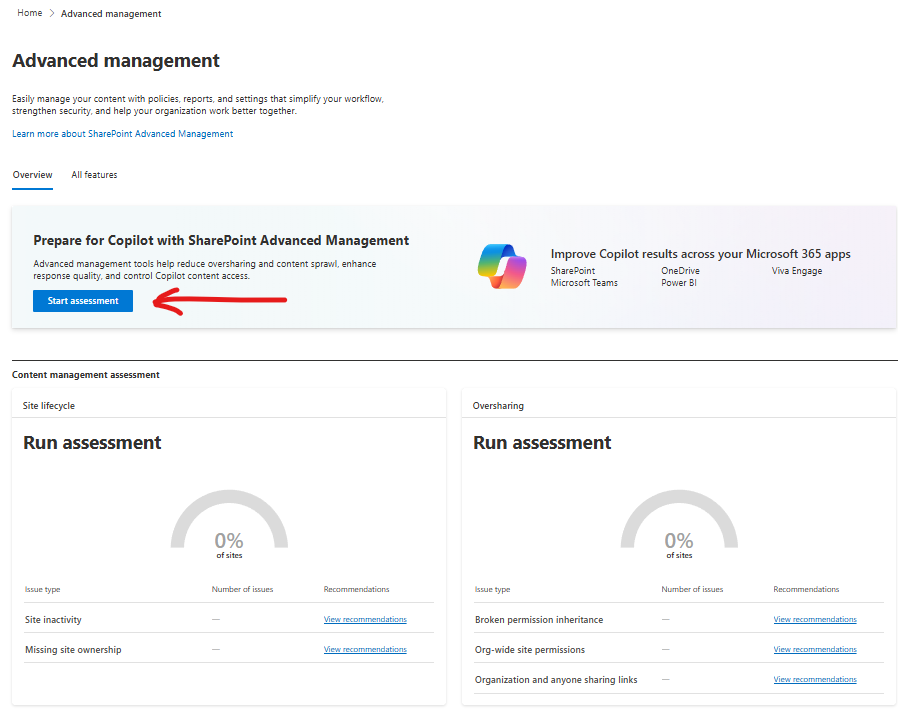
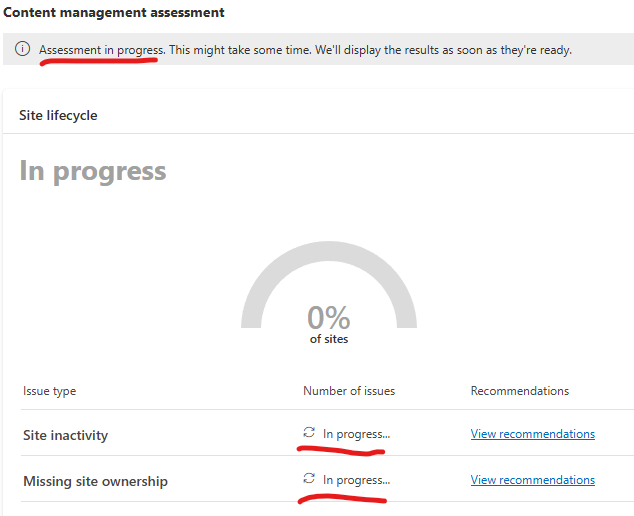
On the “Overview” page Microsoft wants us to run assessment. “Start assessment” button starts assessment immediately. So let us click “Start assessment” button and see what it does exactly. Btw, it might take from days to weeks for your tenant – depending on the tenant size. While assessment is in progress – it’ll display “Assessment in progress. This might take some time. We’ll display the results as soon as they’re ready.”
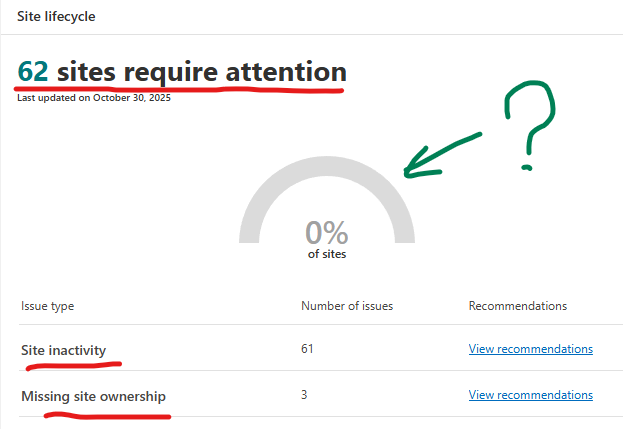
It took 3-4 hours for my small dev tenant to assess Site lifecycle and find 62 sites require attention:
Advanced management – All features
Microsoft classifies SAM’s features as “Manage content sprawl”, “Manage content lifecycle”, “Manage permissions and access”. I’d put SAM’s tools into these buckets: Reports, Policies, Search, Features.
SAM Reports
SharePoint SAM reports provide structured, actionable data that you can analyze to optimize governance strategies and implement immediate improvements. Reports available are:
- Agent Insights – how agents are accessing the content on the sites
- App insights – review apps registered in Entra allowed access to SharePoint sites
- Change history reports – site actions or organization setting changes
you can choose org-wide or site-level settings, specify date range, sites and all or specific admins - Content services reports – Term store, term sets and terms
- Data Access Governance (4 different ones)
- Site permissions across your organization
- Sharing Links with 3 pre-configured reports:
Anyone links, People in your org links and Specific People links shared externally - Sensitivity labels applied to files: select label -> generate report
- Content Shared with Everyone Except External Users:
to discover specific sites whose content was made accessible for EEEU
you can choose from two types of report: where specific files/folders/lists are shared with EEEU or “Site membership” where EEEU was added as a member and initialize access review
(see Deep Dive into SAM DAG Content shared with EEEU access review)
- OneDrive Accounts report – about unlicensed OneDrive accounts
- Site policy comparison – control oversharing by identifying sites with similar files and different policies
SAM Policies
Policies in SharePoint SAM define governance rules that are enforced automatically, minimizing manual intervention and ensuring consistent compliance. SharePoint Advanced Management policies are:
- Site Lifecycle management: Inactive Site Policy. Allows:
- identify inactive sites
- send notifications to site owners and/or admins
- automatically archive or make sites read-only (or do nothing – just report)
(see Deep Dive in SharePoint Inactive Site Policies)
- Site Lifecycle management: Site Ownership Policy (went live June 2025)
(see my SharePoint Site Ownership Policies Deep Dive) - Access control – Site-level access restriction
- Access control – OneDrive access restriction
AI Insights – report feature that uses a language model to identify patterns and potential issues and provide actionable recommendations to solve issues
Features
Features are smaller that policies, more like an update to existing functionality.
- Conditional access to SharePoint site policy
This enhances existing conditional access Entra Id feature with the ability to apply the policy to SharePoint sites directly or via Site sensitivity label. - OneDrive access restriction
- SharePoint site-level access restrictions
- Block download policy
- Your recent actions
- Default sensitivity labels for document libraries
- Site access review
SAM for Search
I put it separately:
- restrict discovery of SharePoint sites and content
- Restricted SharePoint search
TBP