With Microsoft officially announcing the retirement of legacy Azure Access Control Services (ACS), SharePoint administrators are now racing against time. For over a decade, ACS-based permissions—commonly known as SharePoint app-only service principals—have been widely used, with countless tutorials and blog posts guiding users on how to implement them in their applications.
However, many of these ACS-based apps are still actively accessing SharePoint sites. When Microsoft eventually disables ACS, we want to avoid a scenario where critical business processes suddenly break and teams are left scrambling.
To stay ahead of this change, our goal is to identify all app-only principals still relying on ACS to access SharePoint. This includes gathering details about the apps, their owners, the sites they access, and the site owners. The ultimate objective is to proactively reach out to the responsible stakeholders, inform them about the upcoming retirement, and encourage them to migrate their solutions to modern authentication methods.
Technical details
What kind of apps we are talking about, specifically? I can see the following options:
- Apps that were registered in SharePoint via AppRegNew.aspx (aka SharePoint app-only service principals) and provided with permissions in SharePoint via AppInv.aspx
- Apps that were registered in Azure (Entra Id) and provided with permissions in SharePoint via AppInv.aspx
Let us start with pulling data, then I’ll provide step by step instructions how to discover App-Only apps, get these apps activity and actions need to be taken.
Techniques we can use to get data
- analyze audit log to get events where apps are accessing sites
- analyze audit log to get events where ACS permissions were provided to sites
- get data from system that tracks request for new ACS permissions
- use reports from admin center
- use the PnP Microsoft 365 Assessment Tool
- get report on apps owners and permissions from from Entra Id
Let us deep dive into each data source to see if it is actually helps us to get ACS apps in use…
Audit log: apps accessing sites
Microsoft 365 audit log is supposed to save all events happening in Microsoft 365. It is available for admins via GUI, PowerShell Exchange Module and Graph API. GUI Search m365 audit log now lives under Microsoft Purview – Solutions – Audit.
GUI search Audit Log under Purview
Unfortunately, when an App registered in Azure and provided with ACS access (via appinv) is accessing SharePoint sites – no events are saved in m365 audit log.
SharePoint app-only principals (apps registered in SharePoint via appregnew) are tracked in m365 audit log. Events would have a UserId “app@sharepoint” (yes, single user id for all apps). Other event details would include activity/operation (PageViewed, FileModified etc.), Item (full Url of a document or page etc.), AppAccessContext (includes ClientAppid, ClientAppName), ApplicationId (yes, this is how we know what app access what url on the site), and many other details.
Get Audit Log via Microsoft Graph API
The following reports are available via MS Graph API (some as v1.0, others in preview only under beta):
Service principal sign-in activity
This report is available through the servicePrincipalSignInActivity resource type and details the sign-in activity for a service principal in your tenant. The sign-in activity can be delegated or application-only scenarios. For application-only scenarios, the application credential activity provides additional information on the credential usage.
Service principal sign-in activity report provides the following details for every service principal:
- id,
- appId,
- lastSignInActivity,
- delegatedClientSignInActivity,
- delegatedResourceSignInActivity,
- applicationAuthenticationClientSignInActivity,
- applicationAuthenticationResourceSignInActivity
More on Service principal sign-in activity
Application credential sign-in activity
This report is available through the appCredentialSignInActivity resource type and details the usage of an app credential (secret, certificate, or federated identity credential) in your tenant.
Application credential sign-in activity report provides the following details for every service principal credential:
- id, keyId, keyType, keyUsage,
- appId, appObjectId, servicePrincipalObjectId,
- resourceId,
- credentialOrigin,
- createdDateTime,
- expirationDateTime,
- signInActivity
More on Application credential sign-in activity
Audit log ACS permissions provided events
This is relatively easy. There are just two kinds of events that might help us to understand ACS usage in tenant:
SharePointAppPermissionOperation
Pull audit logs with record type is SharePointAppPermissionOperation so you’d get events where permissions were provided to apps. Operation type (activity) would be like AppPermissionGrant.
Microsoft started logging this record type not long ago and there is no documentation found (as of Feb 2025). So the only I noticed that might help is:
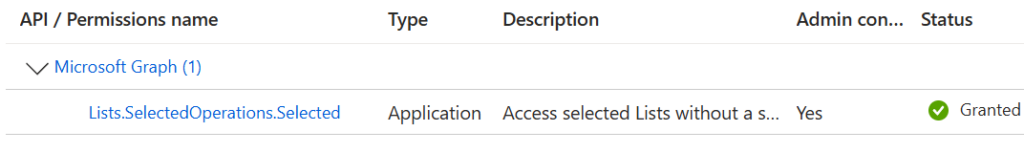
- if user id is “app@sharepoint” – that indicates Sites.Selected permissions were provided to the app
(e.g. via Grant-PnPAzureADAppSitePermission )
under “AppId” you’d have an app (client) id of the client app (permissions provided to) in the form of
“i:0i.t|ms.sp.ext|<appId>@<tenantId>”
under “ApplicationId” and “AppAccessContext – ClientAppId” – you’d have an app (client) id of the admin app (permissions provided via)
ApplicationDisplayName would contain the display name of the admin app
Other fields: RecordType 205, UserType 5, AuthenticationType OAuth
- if user id is one of your actual user’s account in tenant – that indicates ACS permissions were provided to the app (e.g. via appinv.aspx page at SharePoint site)
under “AppId” you’d have an app (client) id of the client app (permissions provided to) in the form of
“i:0i.t|ms.sp.ext|<appId>@<tenantId>”
there would be no “ApplicationId” field and under “AppAccessContext” no ClientAppId
ApplicationDisplayName Unknown
Other fields: RecordType 205, UserType 0, AuthenticationType FormsCookieAuth
Appregnew.aspx and appinv.aspx pages viewed
You can pull audit logs with record type is SharePoint and activity type (operation) is PageViewed and keyword for free search is appregnew. You’d get events when there was an attempt to register a new SharePoint app-only service principal.
The same but with appinv as a search keyword – to get events when there was an attempt to provide ACS permissions for a SharePoint app-only service principal or for an Azure App registration.
In both cases we know that there was an intention to have a principal with an ACS access. We can reach these people to inform that ACS is deprecated and so and so. Worst scenario – we notify somebody who already know that.
Some time ago (around mid – 2023) Microsoft by default disabled ability for site owners registering apps and providing permissions in SharePoint via Appregnew.aspx and appinv.aspx. So since then only SharePoint service admins could provide ACS permissions to apps. In this case you’d check with your request tracking system – to whom ACS were provided.
System that tracks request for new ACS permissions
In case you have a process of providing ACS permissions… Process might include tickets to service desk or similar kind of system… Anyway – check if you can get data from that system – like who requested for what app to what site etc…
Reports available from Microsoft 365 Admin Center
So far the only report that might help is in development (see Microsoft 365 Roadmap – feature Id 417481) and scheduled to be available in May 2025. So far (July 2025) what I can see is the report is not working.
“Enterprise Application Insights is a powerful report which helps SharePoint Administrators to discover all the SharePoint sites that are allowed access by third-party applications registered in your tenant. The report also provides details on the application’s permission and requests count to help admins take further action to strengthen the security of the site. It is part of SharePoint Advanced Management capabilities.”
The feature is already documented here: Generate App insights reports and is seems like the report will not be available for all tenants – but just for tenants with Microsoft SharePoint Premium (SharePoint Advanced Management) or Copilot license assigned.
PnP Microsoft 365 Assessment Tool
Microsoft 365 Assessment Tool is an utility designed by PnP team a while ago and since then serves SharePoint admins very well. In particular, it helps us identify and evaluate the Azure ACS usage for tenant by providing the usage data of ACS principals, and even generating a Power BI reports.
If you run this tool specifying AddInsACS mode, it provides you with:
- classicacsprincipals.csv report that includes all apps with access to SharePoint. Details are: App Ids, if the app has Tenant or Site Collection Scoped Permissions, if the app Allows AppOnly, RedirectUri, AppDomains and ValidUntil
If the ValidUntil field contains specific date – that means the app was registered via appregnew
If the ValidUntil field contains “01/01/0001 00:00:00” date – that means the app was registered in EntraId
if the AllowAppOnly field equals TRUE – that means ACS permissions were provided to the app
- classicacsprincipalsites.csv – report contains apps and sites they have access to
Details are: AppIdentifier, ServerRelativeUrl
- classicacsprincipalsitescopedpermissions.csv – list of apps permissions to sites
Details: AppIdentifier, ServerRelativeUrl, SiteId, WebId, ListId, Right (Read/Write/FullControl/Guest etc.)
If the WebId field equals zeros, that means permissions were provided to entire site collection
- classicacsprincipaltenantcopedpermissions.csv – list of apps with tenant-wide permissions
- some other reports, like list of sites, list of webs
Unfortunately, this tool does not provide when the app was last time authenticated or when the app accessed the site. Also, we do not know what kind of access was provided for the app to the site – Sites.Selected or ACS. If at least one access provided for the app was ACS-based – the app will have AllowAppOnly field equals TRUE.
The tool is highly recommended to use: SharePoint Add-In and Azure ACS Assessment
Report on apps owners and permissions from from Entra Id
Using all the methods above – you’d get a list of active service principals that use legacy ACS authentication. But to whom we need communicate to regarding this service principals? Obviously, we are looking for these service principals owners and sites owners.
There are multiple options how to get an app owner from Azure (Entra Id):
Getting sites (teams, groups) owners is a separate challenge – you’d need or a 3-rd party app or a set of custom PowerShell scripts (see How to Get SharePoint and Teams sites owners report with PowerShell).
How to inventory ACS apps (App-Only principals) and get their activity
The most effective way would be
- Use Microsoft 365 assessment tool to gel list of apps that allows AppOnly access
- Use servicePrincipalSignInActivity or appCredentialSignInActivity to get last Sign-In Activity
I use the following PowerShell to start the tool, get status and export reports:
$tenantDomain = "" # "contoso.sharepoint.com"
$clientid = "" #
$certThumbprint = ""
$certPath = "My|CurrentUser|" + $certThumbprint
./microsoft365-assessment.exe start --mode AddInsACS --authmode application --tenant $tenantDomain --applicationid $clientid --certpath $certPath
./microsoft365-assessment.exe status
./microsoft365-assessment.exe report --id <report id> --mode CsvOnly --path ".\ACS-reports"
So you’ll get a list of legacy apps sorted by recent activity. These apps need to be decommissioned. There should be no one App-only service principal or app registration (client id) with legacy ACS permissions provided in tenant.
Communicate to apps owners and site owners
Once you get a list of legacy (ACS/App-Only) apps – pull report on these apps owners.
Having “classicacsprincipalsites.csv” report from m365 assessment tool – you can pull site owners for every app you need to decommission. This is a big topic itself. See details in my article How to prepare your tenant for Azure ACS retirement – Guide for SharePoint Admins
More Observations
Test scenario 1
DisableCustomAppAuthentication is true, i.e. ACS are not allowed in tenant.
SiteOwnerManageLegacyServicePrincipalEnabled -s false, i.e. site owners cannot register apps at sites or provide permissions to app on sites.
It is not possible for admin to go to appregnew.aspx and create an app (app-only spn).
I registered apps in Azure.
It is possible for admin to go to appinv.aspx and “provide” permissions to the azure app registrations.
Connect-PnPOnline works with certificates or with secrets.
Get-PnPSite works only if connection was made with a Certificate (if connection was made with secret – it gives 401 unauthorized).
Test scenario 2
DisableCustomAppAuthentication is false, i.e. ACS are allowed in tenant.
SiteOwnerManageLegacyServicePrincipalEnabled -s false, i.e. site owners cannot register apps at sites or provide permissions to app on sites.
Connect-PnPOnline and Get-PnPSite works with certificates or secrets if ACS access was provided for an app to at least one site.
If there was no ACS permissions provided for the app – Get-PnPSite gives “Access is denied. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070005 (E_ACCESSDENIED))”
Error messages and possible fixes
“Access is denied. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070005 (E_ACCESSDENIED))” – happens if you try to access SharePoint API with an Entra Id app registration that have an API permissions but do not have legacy ACS permissions being authenticated with a secret.
Solution option 1: try authentication with a certificate.
Solution option 2: use Microsoft Graph API.
“The remote server returned an error: (401) Unauthorized.” – happens if you try to access SharePoint API being authenticated with a certificate with an app registration that do not have modern API permissions correctly provided.
Solution: ensure app registration is configured with SharePoint API permissions.
“(403) Forbidden” – happens if you try to access SharePoint API being authenticated with a secret with an app registration that do not have modern API permissions correctly provided.
Solution: ensure app registration is configured with Graph API permissions.
“AccessDenied”,”Either scp or roles claim need to be present in the token.” – happens if you try to access Graph API being authenticated with a secret with an app registration that do not have modern API permissions correctly provided.
Solution: ensure app registration is configured with Graph API permissions.
Get-MgServicePrincipal
Get-MgServicePrincipal returns servicePrincipal objects with properties and relationships.
ServicePrincipalType = ‘Legacy’ indicates service principal was registered in SharePoint (via appregnew.aspx).
An issue with ACS apps discovery when Graph permissions also provided
There was an issue (before late June 2025)
How do we know the ACS permissions are provided for the app to the site? Two great options: appprincipals.aspx and Microsoft 365 assessment tool by PnP.
An app is shown under appprincipals.aspx only in case if ACS access was provided to app but Sites.Selected access was not provided. The moment you provide Sites.Selected access for the app to the site – the app disappears from list of apps under appprincipals.aspx page. The app is not visible for Get-PnPAzureACSPrincipal. PnP M365 Assessment Tool also fails to get list of ACS apps if the site also has Sites.Selected permissions. It does not help if you remove Sites.Selected permissions. This issue is reported to Microsoft and confirmed. Microsoft is working on it. Upd (June 2025) – Microsoft implemented fix, so all should be good now (but if you are seeing “Sorry, something went wrong” trying to access appprincipals.aspx – just wait, they said db needs to be updated as well, it takes time).
A fix, current state and changes
Microsoft deployed a fix and updated databases. So starting July 2025 we can see all apps (legacy, modern, with ACS and with Graph permissions assigned) under appprincipals.aspx page. The good is we finally can see apps, the bad is we cannot differentiate – is this an ACS app or app with permissions provided via Microsoft Graph, also we cannot see permissions.
Microsoft 365 Assessment Tool does a good job, detecting if the app allows App-Only permissions (AllowAppOnly equals true in the report classicacsprincipals.csv). Under reports classicacsprincipalsites.csv and classicacsprincipalsitescopedpermissions.csv, the tool provides what sites every app has access to and what permissions the app has, but again, it does not provide details if permissions were provided with ACS or Microsoft Graph.
References